Around 26.7 percent of women in the age group of 15 to 44 have PCOS and surprisingly 70% of the women suffering from this don’t even know it.
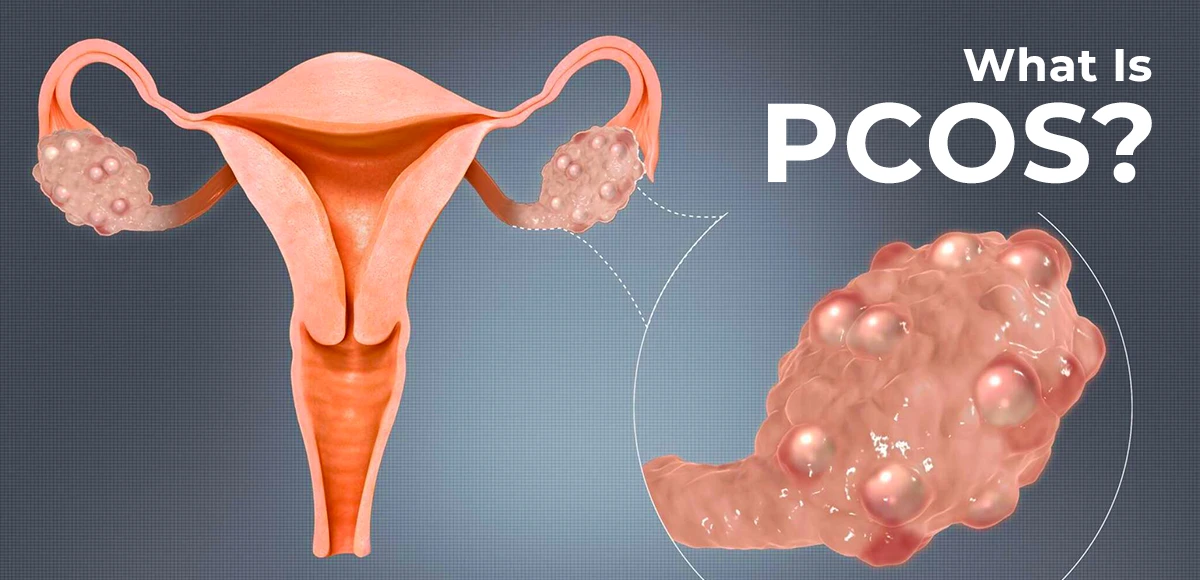
Polycystic ovarian syndrome or Polycystic ovary syndrome is a health problem that is common in women and girls of reproductive age. An imbalance of reproductive hormones causes it, which leads to problems in the ovaries.
The ovaries help the egg that is released every month as part of a healthy menstrual cycle. PCOS restricts the egg from fully developing or may restrict the ovulation process.
Polycystic ovary syndrome can cause missed or irregular periods, and it can lead to:
- Formation of small fluid-filled sacs (cysts) in the ovaries.
- PCOS can even lead to infertility.
Overview Of PCOS:
PCOS (polycystic ovary syndrome) is the most usual cause of infertility in females. It affects 5% to 12% of women of reproductive age in the US. However, this is a lifelong condition that continues far beyond the reproductive years.
With PCOS, women are often insulin resistant, meaning their bodies can’t use insulin effectively, which increases the risk for type 2 diabetes. They also have high levels of male hormones (androgens, which females also have).
Androgen restricts the eggs from being ovulated or released. PCOS can cause several issues, including acne, excess hair growth on the body and face, irregular periods, and thinning of scalp hair.
Overweight women can face some serious health issues related to PCOS, including:
- Diabetes
- Heart disease
- Gestational diabetes (diabetes during pregnancy)
- Stroke
- High blood pressure
- Sleep apnea
- Cholesterol
Symptoms Of PCOS?
The common symptoms and signs of PCOS include:
- Infertility: This is the most common cause. Not ovulating frequently and irregularly ovulating can result in not being able to conceive.
- Cysts: In ultrasound, most of the women with PCOS have ovaries that appear with many follicles and are generally larger (egg sac cysts).
- Irregular Periods: Missing or irregular periods is one of the most common signs. It also involves heavy bleeding during periods.
- Abnormal Hair Growth: Women with PCOS may experience heavy hair growth on their abdomen, arms, and chest area.
- Weight Gain: One of the most common signs is obesity. Women with polycystic ovarian syndrome have trouble maintaining a healthy weight.
- Thinning of Hair: Women with PCOS may experience bald patches on their scalp.
- Acne: Common signs of this disease include acne, which can be seen on your face, chest, and back. These acne can be challenging to treat.
- Darkening of the Skin: You may experience dark skin patches, especially in the folding areas like your neck, between the legs, armpits, and under your breasts.
- Headaches: You may experience headaches with PCOS.
What Causes PCOS?
Doctors don’t know the true cause of PCOS, but factors that might play a role include:
- Heredity: According to researchers, PCOS might be linked with family history, and genes might play an important role in this.
- Increased androgen level: The ovaries may produce high-level androgens with PCOS. This means that eggs do not develop regularly and are not released from the follicles where they are developed.
- Insulin Resistance: Insulin is made by the pancreas. Your blood sugar levels can go up if cells become resistant to the action of insulin. More insulin causes your body to make much of the male androgen hormone. It can cause problems with the ovulation process.
- Low-grade inflammation: White blood cells make substances in response to injury and infection, which is called low-grade inflammation. According to researchers, women with PCOS have a type of low-grade, long-term inflammation, leading to Polycystic ovaries developing androgens. This can also lead to blood vessels and heart problems.
How Is PCOS Diagnosed?
If you are experiencing any of the symptoms mentioned above, you should definitely consult a doctor. Your doctor will ask you about the signs and medical history.
Also, you may have a physical exam, which will likely include a pelvic examination. This exam will help determine the health of your reproductive organs, both outside and inside your body.
Some of the other tests include:
- Blood tests: This test will help to determine high-level androgens and other hormones. Also, your doctor may check your blood glucose levels, and it is important to have your triglyceride and cholesterol levels checked.
- Ultrasound: Ultrasound creates images of tissues, organs, and blood vessels with the help of sound waves and a computer. The images help to determine the size of the ovaries and see if it is a cyst. Also, Ultrasound helps to look at the thickness of the lining of the uterus, endometrium.
How To Treat PCOS?
A number of factors affect the treatment of PCOS. These may include your overall health, how serious your symptoms are, and also your age plays a vital role. The treatment also depends on whether you want to conceive or not in the future.
If you don’t plan to conceive, the treatment may include:
- Birth control medicines: These pills help to lower androgen levels, control menstrual cycles, and reduce acne.
- Change in activity and diet: Maintaining a healthy diet and doing activities can help you lose weight and reduce your PCOS symptoms. Also, this will help your body to use insulin efficiently, help you to ovulate, and lower your blood sugar levels.
- Diabetes Pills: These medications help lower insulin resistance, reduce androgen levels, and ovulate more regularly.
- Pills to treat other symptoms: Many medications can also help you to reduce your acne and hair growth.
If you are planning to get pregnant, the treatment may include:
- A change in activity and diet: Managing your schedule efficiently will surely help you to reduce the symptoms of PCOS. more physical activities and a proper diet can help you to gain a healthy weight. Doing these can help you to use your body insulin more effectively, can lower blood sugar levels, and can help you to ovulate.
- Pills to cause ovulation: Pills help the ovaries to release the eggs normally. However, these pills can have some serious risks involved. They can increase the chance of having twins or more. Also, they can cause ovarian hyperstimulation when the ovaries release too many hormones. Additionally, it can cause symptoms like pelvic pain and bloating.
How To Get Pregnant With PCOS?
You can get pregnant if you are suffering from PCOS. However, you might need some medications to make the ovulation process efficient. Additionally, you can use technologies such as In Vitro Fertilization (IVF).
Medicines that can help you to ovulate:
- Clomiphene (Serophene, Clomid): An anti estrogen drug that is taken at the beginning of your cycle.
- Metformin (diabetes drug): If Clomiphene isn’t helping with ovulation, this medicine can help you.
- Gonadotropins (hormonal medications): Your healthcare provider may prescribe you this medicine if the above-mentioned pills are not working.
- Letrozole (Femara): When other medications do not work, this is used often to treat women.
Other options for improving fertility are:
Surgery:
When ovulation medications don’t work, doctors often recommend surgeries. One of the procedures is called “Ovarian Drilling,” which makes your ovaries work in a better way.
The surgery includes making a small cut in your belly and removing those parts of your ovaries that make high-level androgens. However, this procedure is not very popular now because there are many medications available on the market.
IVF (In Vitro Fertilization):
This is a popular procedure in which your doctor removes one of your eggs and then combines it with your partner or a donor.
After that, the fertilized egg is placed back in your uterus. This procedure is a bit expensive but is also the most effective way to conceive if you have PCOS.
Diet and Lifestyle Changes For PCOS and Fertility:
A healthy lifestyle can surely help you to cure your PCOS and fertility. Some of the elements that you can incorporate into your daily life are:
Weight Management:
Not every PCOS patient is overweight, but most of them are. If you are overweight or obese, weight loss will help you manage your hormone levels. Losing only 10% of your total body weight can help you to have a regular menstrual cycle.
Your doctor may recommend you to choose food that is lower in calories. However, losing weight is not an easy task but a dietician or a nutritionist can help you.
PCOS Diet:
For managing your blood sugar levels, doctors often suggest focusing on foods that are less in sugar level and specific carbs (carbohydrates). Some carbs, such as those in high-fiber vegetables and fruits, are good for you.
However, refined carbs should be limited, including white rice, highly processed foods, white flour, sugar, or white potatoes. These foods can make your blood sugar level rise quickly. You can choose healthy options such as lean meats, poultry, whole grains, and fish.
Exercise:
Regular exercise helps to boost your self esteem and mood. It also helps you to burn calories, lower androgen levels, and decrease insulin resistance.
Getting Proper Sleep:
Make sure to get enough sleep. Ensure you don’t stay awake for hours and sleep in a quiet, dark, and comfortable room.
Some Other Factors To Keep In Mind:
- Limiting Caffeine: Up to about 4 cups of caffeine intake are fine. If you are consuming more than that, it can affect your health and sleep.
- Reduce stress: PCOS can be stressful sometimes, but if you don’t try to control your stress levels, the disease can become worse. Stress can also lead to some of the common issues, depression and weight gain. Exercise, yoga, and various mindful meditation can help you to reduce your stress levels.
- Avoid Endocrine disruptors: Endocrine disruptors are chemicals that are thought to cause hormonal imbalances. Some common ones are triclosan, phthalates, and parabens.
They are commonly found in pesticides, industrial chemicals, plastics, and chemicals. It is quite difficult to avoid these chemicals, but there are some ways to reduce your exposure, including:
- Avoid products with fragrance
- Avoid canned foods lined with BPA
- Store foods in stainless steel or glass and avoid plastic containers
- Before eating food, wash your hands properly
- Use HEPA filter vacuum
PCOS vs PCOD
PCOS and PCOD may sound similar, but they are a bit different from each other. In Polycystic ovarian disease (PCOD), the ovaries release immature eggs, leading to several hormonal imbalances and swollen ovaries.
On the other hand, in Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), endocrine issues cause ovaries to produce excessive amounts of androgens, making the eggs prone to become cysts (fluid-filled sacs). However, in PCOD, these cysts do not release but build up in the ovaries.
| PCOD | PCOS |
| PCOD is a common disorder | PCOS is a serious medical condition |
| PCOD is a disorder in which ovaries produce many immature or partially mature eggs | PCOS is a metabolic disorder when ovaries stop releasing eggs. |
| PCOD doesn’t cause infertility. | PCOS can cause infertility. |
| PCOD doesn’t have any serious complications. | PCOS can cause serious complications such as type 2 diabetes, heart disease, high-blood pressure and endometrial cancer in later stages. |
Conclusion:
PCOS can affect a woman’s menstrual cycle and make it harder for them to get pregnant. High levels of androgen also lead to serious issues like unwanted hair growth on the face and body. However, there are many treatments available that can surely help you to conceive.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs):
- Is PCOS Treatable or not?
Polycystic ovary syndrome can not be cured, but its symptoms can be managed. You can schedule your day with some activities and a healthy diet, which will surely help you in the future.
- Is PCOS lifelong?
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) is often poorly understood and misdiagnosed. This is a lifelong disorder that can be definitely managed by a healthy lifestyle and medications.
- Do PCOS cysts go away?
Although PCOS is not curable but a proper diet, several medications, and a healthy lifestyle can help you to fight with some of the issues related to it.
- Can I live a long life with PCOS?
Several studies have shown that women with PCOS had an increased risk of death due to endocrine as well as tumors, metabolic diseases, cardiovascular diseases, and nutrition.
Meta Description: PCOS is a common type of hormonal imbalance in women, causing several health issues like irregular periods, but these issues can be managed, here are a few tips.